What Best Describes the Citric Acid Cycle
4 Which of the following best describes the importance of the citric acid cycle as a central pathway of metabolism. It allows recovery of energy from carbohydrates only.

Resumen Del Ciclo De Calvin Benson Paperblog Photosynthesis Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol and the electron transport chain involves both the intermembrane space and the inner mitochondrial membrane.
. Transfer of energy via electrons in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions to make ATP c. This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose. The citric acid cycle also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle is a series of chemical reactions in the cell that breaks down food molecules into carbon dioxide water and energy.
The formation of glucose de-novo from other molecules O b. Which of the below best describes the citric acid cycle. This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration.
The citric acid cycle CAC also known as the TCA cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates fats and proteinsThe Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire as opposed to organisms that ferment to generate energy either by anaerobic. This pathway produces NADH and FADH2 which enter through chemiosmosis. Researchers suspect that portions of the reverse cycle may have been responsible for fixing CO2.
The citric acid cycle or TCA cycle Tricarboxylic acid or Krebs cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl CoA 2C with oxaloacetate 4C to produce citrate 6C. The citric acid cycle is the process by which acetyl-CoA a two-carbon molecule is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and energy. Many bacteria perform the.
This cycle produces NADH and FADH _2 which donate electrons to the electron transport chain to pump protons. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose. View the full answer.
This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose. Which statement best describes how the citric acid cycle relates to glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis. Glycolysis produces pyruvate which is converted to acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle.
Citric Acid Cycle 1Product of one complete round of the citric acid cycle 2Glucose residues linked together 3Oxidizes Acetyl groups to carbon dioxide 4The final result of glycolysis 5Two-carbon fragments derived from carbohydrates amino acids and. The electrons temporarily stored in molecules of NADH and FADH 2 are used to generate ATP in a subsequent pathway. Which statement describes the citric acid cycle.
A is the reaction of the citric acid cycle that occurs spontaneously without enzymatic catalysis. From there the following occurs. The citric acid cycle is a series of redox and decarboxylation reactions that remove high-energy electrons and carbon dioxide.
The citric acid produces pyruvate which converts to glucose to enter glycolysis. From a general summary to chapter summaries to explanations of famous quotes the SparkNotes The Citric Acid Cycle Study Guide has everything you need to. In plants and animals eukaryotes these reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria of the cell as part of cellular respiration.
It allows recovery of energy from fatty acids only C. Oxidative phosphorylation the process where electron transport from the energy precursors from the citric acid cycle step 3 leads to the phosphorylation of ADP producing ATP. Oxygen is required to regenerate electron acceptors Citrate is dehydrated and hydrated by the same enzyme aconitase.
Up to 10 cash back The citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. It allows recovery of. Which of the following best describes how the citric acid cycle relates to glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
The last part of. Which of the following best describes the importance of the citric acid cycle as a central pathway of metabolism. This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration.
Researchers suspect that the original citric acid cycle was used by all species. C converts a tertiary alcohol which cannot easily be oxidized to. Acetyl-CoA loses its CoA and is attached to oxaloacetate OAA to produce citrate which is converted to isocitrate.
Pyruvate from glycolysis is transported into the mitochondrial matrix for the citric acid cycle. In prokaryotes these steps both take place in the cytoplasm. It allows recovery of energy from carbohydrates only B.
This cycle produces the energy currency that undergoes the electron transport chain to produce water and ATP. The isomerization of citrate to isocitrate. O A The citric acid produces pyruvate which converts to glucose to enter glycolysis.
D Glycolysis produces pyruvate which directly enters the citric acid cycle. The reactions of the cycle are carried out by eight enzymes that completely oxidize acetate a two carbon molecule in the form of acetyl-CoA into two molecules each of carbon dioxide and water. The ATP produced is utilized in large amount in the process of glycolysis.
This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose. Breakdown of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate d. This produces ATP by pumping protons through chemiosmosis.
Biology questions and answers. One molecule of either GTP or ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation on each turn of the cycle. Which statement describes the citric acid cycle.
Coenzymes are reduced in the citric acid cycle. Citric acid produces NADH and FADH2 which undergo oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway produces NADH and FADH2 which enter oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP through chemiosmosisc.
Which is oxidised in a series of steps to release two CO 2 molecules and oxaloacetate is regenerated back to continue the cycle. The citric acid cycle where acetyl CoA is modified in the mitochondria to produce energy precursors in preparation for the next step. The citric acid cycle is a closed loop.
Researchers suspect that early methods for converting pyruvate to. In eukaryotes the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria just like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl. B protects cells from the toxic effects of arsenite ion.
Up to 10 cash back Correct answer. Which of the following correctly describes the citric acid cycle.

Lesson Explainer The Link Reaction And Krebs Cycle Nagwa

Schematic Representation Of The Citric Acid Cycle And The Mitochondrial Download Scientific Diagram

6 25 The Citric Acid Cycle Nutrition Flexbook

Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Biochemistry Britannica

Lesson Explainer The Link Reaction And Krebs Cycle Nagwa

Cellular Respiration Overview Video Tutorial Biology Classroom Science Cells Science Biology

The Citric Acid Cycle Article Khan Academy

Hd Animations Dr Prodigious Cellular Respiration Krebs Cycle Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Stain Removing Hacks That Work For Toddlers Cleaning Hacks House Cleaning Tips Cleaning
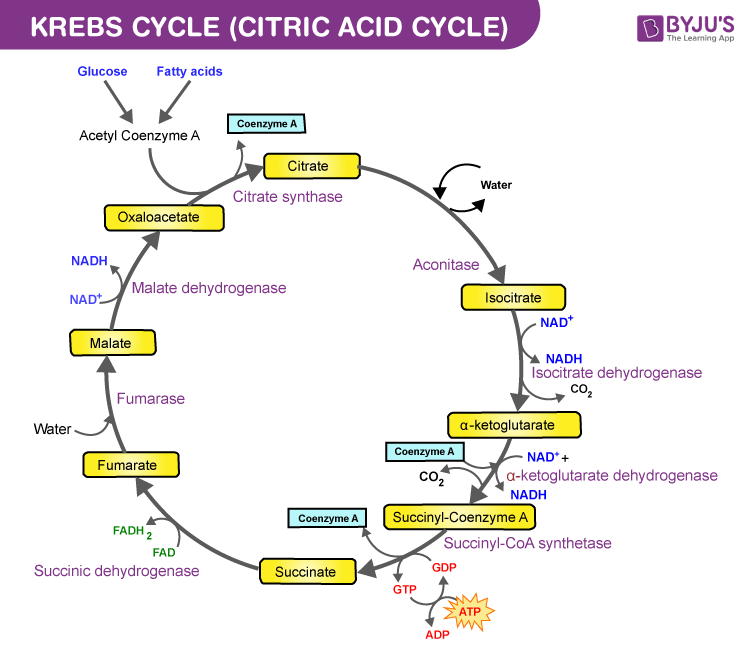
Krebs Cycle Or Citric Acid Cycle Steps Products Significance

In The Citric Acid Cycle Does Fadh 2 Become Reduced During Step 6 Study Com
Can You Explain The Citric Acid Cycle Or Krebs Cycle In Simple Terms Quora
4 3 Citric Acid Cycle And Oxidative Phosphorylation Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

In The Citric Acid Cycle Cis Aconitic Acid Is Formed As An Intermediate Download Scientific Diagram
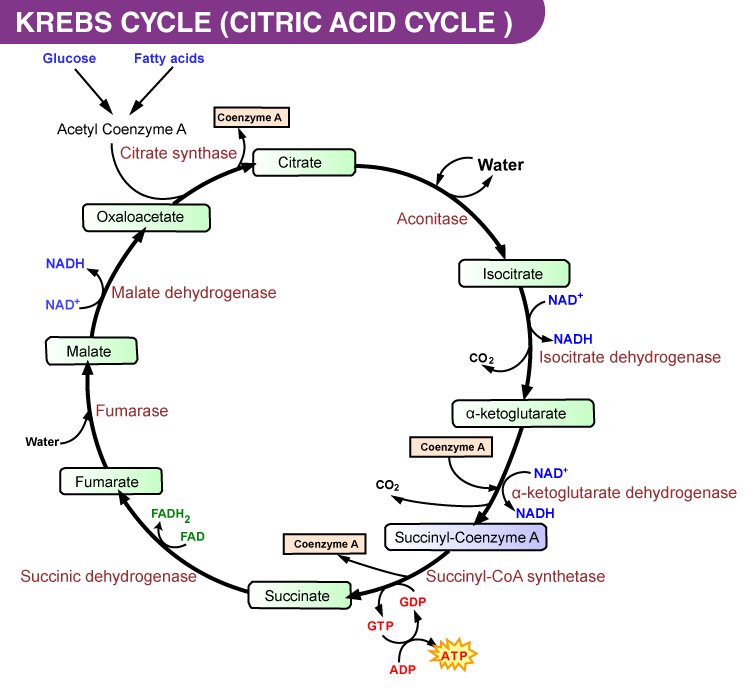
What Happens In The Citric Acid Cycle Get The Answer At Byju S Neet

The Citric Acid Cycle 7 3 Tca Cycle Regulation Flashcards Quizlet


